Physics of Weight Distribution
Weight Distribution
 Weight Distribution is the allocating of weight within a vehicle whether it be an airplane, train or car. This distribution of weight directly affects many aspects of a vehicle in motion. For instance, it affects a car's handling, acceleration, and traction.
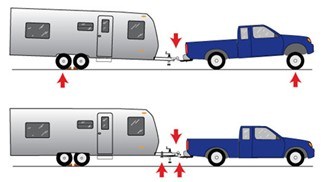
Weight Distribution is the allocating of weight within a vehicle whether it be an airplane, train or car. This distribution of weight directly affects many aspects of a vehicle in motion. For instance, it affects a car's handling, acceleration, and traction.Most commonly, the principle of weight distribution is used when you're hauling a trailer behind your car. When towing a trailer, the trailer's weight is transferred to the rear axle of your car. Thus resulting in the back end of the vehicle being forced lower to the ground and the front end to become raised. If this were to occur, the your vehicle's rear axle will not only bear the weight of your vehicle, but also the trailer. However, if the front axle were to have less weight on it, you can experience diminished performance in steering, traction or braking.

If you do not distribute your weight evenly you may experience dangerous effects, including: Reduced braking performance, Less traction, Reduced steering, Reduced traction of front wheels, Incorrect wheel alignment, and Increased risk of rollover. However, the even distribution of weight results in a smooth ride, as well as the ability to tow at the maximum capacity of your hitch.
Demonstrating the Effects of Good and Poor Weight Distribution:
Why This Happens:
This reaction can be explained with the principle of torque. Torque is the cross product of Force and Radius... T = RxF. Think of the Trailer as a bar, and the further the weight is from the axle (or the hitch connected to the towing vehicle) the more torque will be applied to this one spot because the radius has been increased. Since every force has an has an equal and opposite reaction, there will be a force pushing back on this torque. However, there is not enough force in the front to cancel out the torque caused as a result of this swaying. The trailer rotates about it's axles. If the weight is distributed forward of the trailer axle, the direction of the force at the hitch helps to self correct. With the weight distributed behind the axle, the force at the hitch is now opposite. This drives the oscillation and the constant swaying back-and-forth. In other words, if weight is not distributed correctly there is not enough force towards the front of the trailer to cancel out the swaying and "correct" itself.
Real-World Applications
 Airliners use the principle of weight distribution to evenly spread the weight of passengers, cargo, and fuel throughout the aircraft so as to keep the aircraft's center of gravity close to its center of pressure to prevent losing pitch control. Also, in the military loadmasters position cargo precisely so as to properly secure cargo and prevent it from shifting.
Airliners use the principle of weight distribution to evenly spread the weight of passengers, cargo, and fuel throughout the aircraft so as to keep the aircraft's center of gravity close to its center of pressure to prevent losing pitch control. Also, in the military loadmasters position cargo precisely so as to properly secure cargo and prevent it from shifting.🐒 🏈
Bibliography:
1. http://www.pedders.com.au/kits/importance-weight-distribution#
2. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4jk9H5AB4lM&ab_channel=svovik1

Comments
Post a Comment